What is a Derivative in calculus?
Derivative is the slope at a point on a line around the curve. It is a fundamental tool of
calculus.
calculus.

The derivative is called an Instantaneous rate of change that is, the ratio of the instant
change in the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable.
change in the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable.
If f(x) is the function then the derivative of it will be represented by fꞌ(x).
Who found the Derivative?
Calculus was discovered by Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz in 17th Century.
But it was not possible without the early developments of Isaac Barrow about the derivatives
in 16th century.

Isaac Newton (1642-1727)

Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716)
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz introduced the symbols dx, dy, and dx/dy in 1675.This shows the functional relationship between dependent and independent variable.
But it was not possible without the early developments of Isaac Barrow about the derivatives
in 16th century.

Isaac Newton (1642-1727)

Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716)
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz introduced the symbols dx, dy, and dx/dy in 1675.This shows the functional relationship between dependent and independent variable.
Joseph Louis Lagrange introduced the prime notation fꞌ(x).
These two are the commonly used notations. There are two more notations introduced by
Newton and Euler.
Newton’s Notation ẏ
Calculus comes from the Latin word which means small stones. Here
differential calculus is to cut something into small pieces to find how
it changes.
Basically, derivatives are the differential calculus and integration is the integral calculus.
Derivatives tell us the rate of change of one variable with respect to another.
What does it mean to differentiate a function in calculus?
Differentiation means to find the rate of change of a function or you can say that the
process of finding a derivative is called differentiation.
process of finding a derivative is called differentiation.
For Example:
Speed tells us how fast the object is moving and that speed is the
rate of change of distance covered with respect to time. So we can say
that speed is the differentiation of distance with respect to time.
To differentiate a function, we need to find its derivative function using the formula.
To differentiate a function, we need to find its derivative function using the formula.

Here x∈ (a, b) and f is differentiable on (a,b).
We had studied about the computation of derivatives that is, how
to find the derivatives of different function like composite functions,
implicit functions, trigonometric functions and logarithm functions
etc.
But now in the application of derivatives we will see how and where to apply the concept
of derivatives.
of derivatives.
Generally the concepts of derivatives are applied in science, engineering, statistics
and many other fields.
and many other fields.
Some of the applications of derivatives are:
To find the rate of change of a quantity
For Example, to find if the volume of sphere is decreasing then at what rate the radius will
decrease.
decrease.
If we have one quantity y which varies with another quantity x, following some rule that is, y = f(x), then


represents the rate of change of y with respect to x.
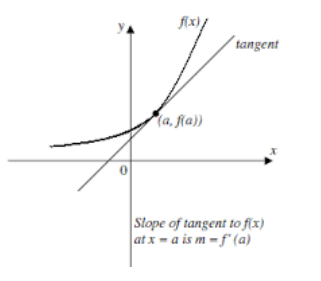
To find equation of tangent and normal for a curve at a point
Tangent is a line which touches a curve at a point and if it will be extended then will
not cross it at that point.
not cross it at that point.
Normal is line which is perpendicular to the tangent to the curve at that point.


The equation of a line passes through a point (x1, y1) with finite slope m is
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
As we know that if the function is y = f(x) then the slope of the tangent to the curve at point (x1, y1) is defined by fꞌ(x1).
So, the equation of the tangent to the curve at point (x1, y1) will be
y – y1 = fꞌ(x1) (x – x1)
and as the normal is perpendicular to the tangent the slope of the normal to the curve
y = f(x) at (x1, y1) is
y = f(x) at (x1, y1) is

So the equation of the normal to the curve is


To find the interval in which a function is increasing or decreasing
On an interval in which a function f is continuous and differentiable, a function will be
This helps to find the turning points of the graph so that we can find that at what point the graph reaches its highest or lowest point. This helps in drawing the graph.

- Increasing if fꞌ(x) is positive on that interval that is, dy/dx >0
- Decreasing if fꞌ(x) is negative on that interval that is, dy/dx < 0
- Constant if fꞌ(x) = 0 on that interval.
This helps to find the turning points of the graph so that we can find that at what point the graph reaches its highest or lowest point. This helps in drawing the graph.
- At x= c if f(x) ≤ f(c) for every x in the domain then f(x) has an Absolute Maximum.
- At x = c if f(x) ≤ f(c) for every x in in some open interval (a, b) then f(x) has a Relative Maximum.
- At x= c if f(x) ≥ f(c) for every x in the domain then f(x) has an Absolute Minimum.
- At x = c if f(x) ≥ f(c) for every x in in some open interval (a, b) then f(x) has a Relative Minimum.

Here in the above figure, it is absolute maximum at x = d and absolute minimum at x = a.
Relative maximum at x = b and relative minimum at x = c.
Relative minimum and maximum will collectively called Relative Extrema and absolute minimum and maximum will be called Absolute Extrema.
We use differentiation to find the approximate values of the certain
quantities. If there is a very small change in one variable correspond
to the other variable then we use the differentiation to find the
approximate value.
The differentiation of x is represented by dx is defined by dx = x where x is the minor change in x.
The differential of y is represented by dy is defined by (dy/dx) ∆x = x.
As x is very small compared to x, so dy is the approximation of y.hence dy = y.
Real life Applications of Derivatives
The odometer and the speedometer in the vehicles which tells the driver the speed and distance, generally worked through derivatives to transform the data in miles per hour and distance.
In the business we can find the profit and loss by using the derivatives, through converting the data into graph.
In physics it is used to find the velocity of the body and the Newton’s second law of motion is also says that the derivative of the momentum of a body equals the force applied to the body.
To find the change in the population size, we use the derivatives to calculate the growth rate of population.
In economics, to find the marginal cost of the product and the marginal revenue to the company, we use the derivatives.For example, if the cost of producing x units is the p(x) to the company then the derivative of p(x) will be the marginal cost that is, Marginal Cost = dP/dx
In geology, it is used to find the rate of flow of heat. Like this, derivatives are useful in our daily life to find how something is changing as “change is life.”
=====================================================================
NOW IF YOU ARE SOLVING
BEST REVISION BOOK OF MATHEMATICS BY ER. SHAMBHU KUMAR BELOW LINK MAY BE USEFUL TO YOU.


No comments:
Post a Comment